Compartive effectiveness of robot-interactive gait training with and without ankle robotic control in patients with brain damage
Abstract
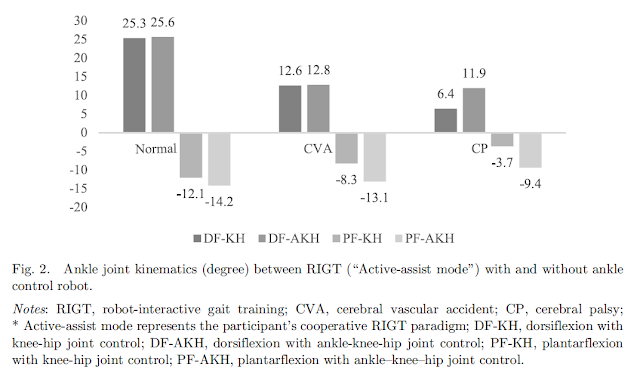
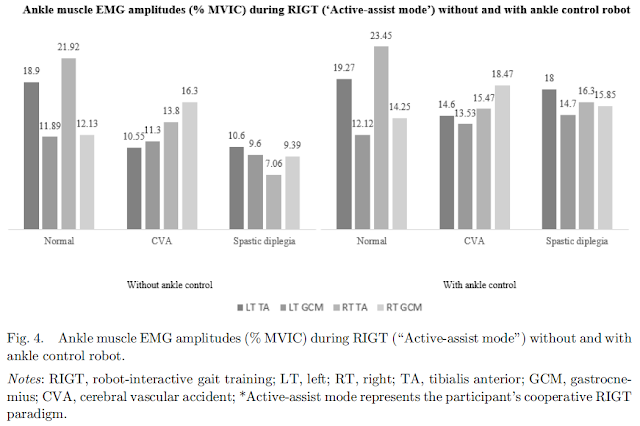
Although ankle robotic control has emerged as a critical component of robot-interactive gait training (RIGT), no study has investigated the neurophysiological and biomechanical effects on ankle muscle activity and joint angle kinematics in healthy adults and participants with brain damage, including stroke and cerebral palsy (CP). This study compared the effects of RIGT, with and without ankle control actuator, on ankle muscle activity and joint angle kinematics in healthy adults and participants with brain damage. Ten patients (healthy ¼ 4, left hemiparetic stroke ¼ 3, CP ¼ 3) underwent standardized surface electromyography (EMG) neurophysiological and kinematics biomechanical tests under the RIGT with and without ankle control actuator conditions. Outcome measures included the EMG amplitudes of the tibialis anterior and gastrocnemius muscle activity, and ankle movement angles recorded with a two-axis digital inclinometer. Descriptive statistical analysis demonstrated that RIGT with ankle control actuator showed superior effects on EMG (30%) and kinematics angles (25%) than RIGT without ankle control actuator. Our results provided novel, promising clinical evidence that RIGT with ankle control actuator can more effectively improve the neurophysiological EMG data and ankle dorsiflexion and plantarflexion movements than RIGT without ankle control actuator in participants with stroke and CP.
Conclusion
The clinical case series study demonstrated that RIGT with ankle control actuator is more effective in improving ankle EMG-controlled dorsiflexion and plantarflexion than RIGT without ankle control actuator in participants with stroke or CP. Our results provided clinical evidence-based insights on the utilization of robot interactive locomotor training with ankle control to maximize and develop recovery of ankle–knee–hip joint movement control, thereby improving walking safety, preventing falls, and thus, improving the quality of life and the activities of daily living.
View "발목 로봇제어 유무에 따른 뇌손상 환자의 로봇 인터랙티브 보행 훈련(워크봇) 비교 효과"
#WALKBOT #RobotAssistedGaitTraining #RoboticGaitTraining #LowerLimbRehabilitationRobot #RoboticRehabilitation #GaitTraining #RehabilitationRobot #Rehabilitation #Stroke #CerebralPalsy #Neuroplasticity

Comments
Post a Comment