Robotic-assisted gait training schematic guideline based on baseline functional ambulatory category level
The RAGT(Robotic assisted gait training) schematic guideline is purported to provide robotic therapists with the appropriate clinical decision-making tools to select the optimal mode of locomotor rehabilitation robotics for the patient’s baseline ambulation level.
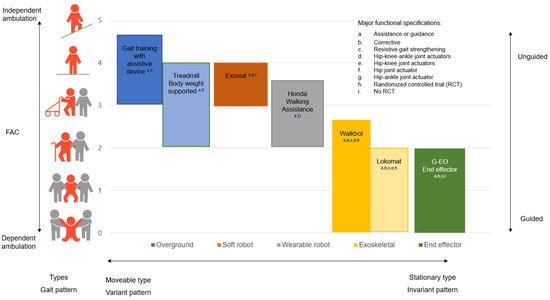
Briefly, the RAGT schematic guideline is comprised of three core elements as follows:
the patient’s baseline ambulation capacity, appropriate RAGT type, and amount of assistance provided. Baseline ambulation function is defined by FAC. Further, commercialized RAGTs can be categorized by type and gait pattern, from a “moveable type” or “more variant gait pattern” (overground treadmill gait, soft robot, and wearable robot) to a “stationary type” or “more invariant gait pattern” (exoskeletal robotics).
An overground robotic device is based on the concept of assistance and facilitation of trunk control and lower limbs’ muscle activation pattern even in individuals with the low FAC levels (0–1), while RAGT aims at the mitigation of the abnormal synergistic gait via an intensive ankle-knee-hip interlimb locomotor coordinated training. HFAC(FAC ≥ 2, high initial functional ambulation category) can perform intensive activities in ground-based robotic devices because of the aforementioned neurophysiological factors and neurobiological changes.
In the case of static RAGT, this will be helpful for LFAC(FAC < 2, low initial functional ambulation category) because it enables intensive training and can help the patient’s weight and muscle strength. However, our study also confirmed the improvement of HFAC in the Walkbot RAGT.
The soft robot includes the Exosuit (Rewalk Robotics, Yokneam, Israel), whereas wearable robots comprise the Honda Walking Assistance (Honda, Tokyo, Japan; hip control only), Ekso bionics (Ekso bionics, Richmond, USA; knee-hip control). The “stationary” exoskeletal robotics include the Walkbot (ankle-knee-hip control), Lokomat (hip-knee control only), G-EO (Reha Tech AG, Olten, Switzerland; end-effector, foot control only), Gait trainer (RehaStim, Berlin, Germany; end-effector, foot control only), and gait-assistance robot (Toyota, Tokyo, Japan; hip-knee control only)].
The “amount of assistance or guidance” (unguided or partially guided) systematically varies depending on the patient’s ability to move the interlimb ankle-knee-hip joint within the predefined “ideal kinematic and kinetic locomotor trajectory” in a coordinated fashion.
Comments
Post a Comment